Cash Flow Hedging Strategies: An Overview of Benefits and Risks

Companies that are exposed to market risks say foreign currency volatility, are more prone to incurring losses due to abrupt changes in the value of the currency they are dealing with. To hedge themselves, they use financial instruments, such as forward contracts, options, or futures as a part of their hedge accounting policy. In conclusion, a cash flow hedge is a valuable tool that companies use to mitigate the risk of cash flow fluctuations. By understanding this concept, traders can gain insights into a company’s financial strategy and risk management practices, which can inform their investment decisions. Commodity price hedges are used to protect against the risk of changes in commodity prices.
Managing the Cash Flow Hedge Reserve Account
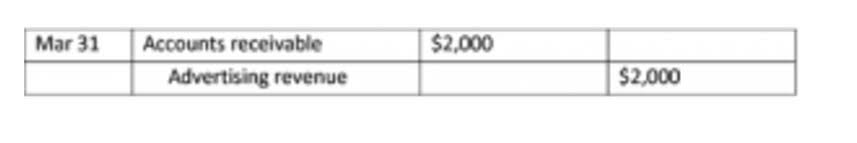
- The accounting for a cash flow hedge for the hedged item is to initially recognize the effective portion of any gain or loss in other comprehensive income.
- By entering into options contracts, businesses can protect themselves from adverse price movements, ensuring a level of predictability in their financial performance.
- The measurement of hedge effectiveness must be consistent with company’s risk management strategies and the method of assessing hedge effectiveness that company has initially documented.
- For example, a retailer may decide to hedge its exposure to commodity price fluctuations by entering into futures contracts.
- Investors must also provide details regarding the risk and the date, or period of time, in which the cash flow would occur.
This integration is not merely a financial maneuver but a strategic move that aligns with the company’s risk management objectives and overall business goals. From the perspective of a financial controller, the primary goal is to align the hedge with the exposure it is meant to mitigate. This means identifying the specific cash flow risks and choosing the right hedging instruments that effectively offset these risks. For instance, if a company has significant expenses in a foreign currency, it might use forward contracts to lock in the exchange rate for future payments, thus avoiding the risk of currency fluctuations. Cash flow hedging typically involves financial tools designed to offset changes in future cash flows. The most common instruments include Foreign Currency Translation derivatives, such as futures contracts, options, and swaps.
- So here, you have some “fixed item” and you’re worried that its value will fluctuate with the market.
- If eligible, the entity may elect to designate its interest rate swap as a hedge for accounting purposes.
- To lock in interest rates on variable rate debt, companies can enter into an interest rate swap designated as a cash flow hedge.
- Discover how to implement high-value cash forecasting with GTreasury’s comprehensive guide.
Cash Forecasting Data Visualizations

Since there was no ineffectiveness, there is nothing to recognize in profit or loss. At the time of the sale on 31 May 20X5, it is necessary to calculate the fair value of the derivative first and recognize its fair value gain or loss. And when it comes to hedging fixed items, then you’re practically dealing with the fair value hedge.
Cash flow hedge vs fair value hedge
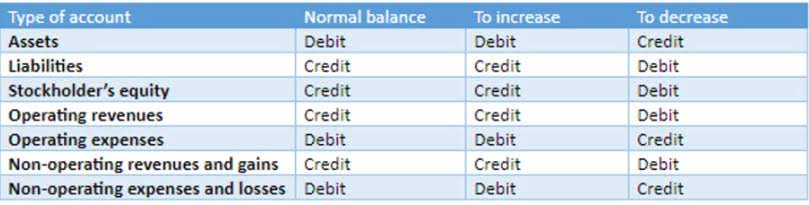
Under fair value hedge accounting, changes in the fair value of the hedging instrument and the hedged item are recorded in the income statement to reflect the economic relationship between the two. This stringent framework ensures transparency in hedging disclosures, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the financial health of the bookkeeping company. If we want to manage the risk of our assets, liability, debtors, creditors, stocks, shares, etc., we have to enter into a hedging contract.
- It may be worth looking at an in-depth cash flow hedge example to see how this works in a practice.
- The timing of taxable gains or losses is delayed until the hedged transaction affects earnings, according to Example 1.
- Foreign exchange hedges are used to protect against the risk of changes in foreign exchange rates.
- Nevertheless, use of the shortcut method in fair value hedges has remained very popular due its accounting simplicity and lower administrative burden.
How is Hedge Effectiveness Assessed?
These gains and losses are initially recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI), a section of equity separate from net income. The most common types of cash flow hedges are foreign exchange hedges, interest rate hedges, and commodity price hedges. Each of these hedges is designed to protect against a specific type of risk and involves the use of specific financial instruments. For example, consider a U.S. company that has a significant amount of revenue in euros. The company is concerned about the potential impact of exchange rate fluctuations on its cash flows. To protect itself from this risk, the company enters into a forward contract to sell euros and buy U.S. dollars at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date.
- Financial reporting for cash flow hedges is a bit more complex than other types of financial instruments.
- Find below a detailed comparison of the differences between a cash flow hedge and a fair value hedge.
- If the wall is effective, the accumulated gains or losses in OCI are released to the income statement.
- When it comes to managing risk with cash flow hedging strategies, implementation plays a crucial role.
- Since almost all of Platform’s costs are denominated in USD, it enters into a 3-month forward contract to sell EUR 3,000,000 forward at USD1.5/EUR.
- The usual business activities of companies and their customers are changing and may not be able to be predicted at this point in time, and expected hedge relationships may be going away.
- In summary, cash flow hedges are an important risk management tool for businesses looking to minimize uncertainty and volatility in their future cash flows from anticipated business activities.
How to Extend the Cash Flow Projection Horizon
Financial reporting cash flow hedge vs fair value hedge for cash flow hedges is a bit more complex than other types of financial instruments. You record changes in the hedge’s fair value in OCI, then transfer them to earnings when the hedged transaction impacts profit or loss. Companies use cash flow hedges to minimize risk and stabilize cash flows from variable rate assets and liabilities. A reliable cash flow forecast is essential for determining the appropriate hedging instruments and their timing. By comparing the actual cash flows with the forecasted ones, companies can assess the effectiveness of their forecasting models. For example, if a company consistently overestimates its cash inflows, it may lead to ineffective hedging decisions, resulting in potential losses.
This stabilizes their future interest cash flows and records fluctuations in the swap’s fair value in other comprehensive income rather than net income. In terms of accounting treatment, changes in the fair value of the hedging instrument and hedged item are recognized in profit or loss simultaneously, offsetting each other. This is in contrast to cash flow hedges, where changes in the fair value of the hedging instrument are recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI) and reclassified to profit or loss when the hedged item affects profit or loss. A cash flow hedge is used to minimize the risk of future cash flow fluctuations arising from an already-held asset or liability or a planned transaction. This type of hedge can qualify for hedge accounting if the changes in the cash flow can potentially affect the income statement.







